Biography
Biography: Dominique Ausserré
Abstract
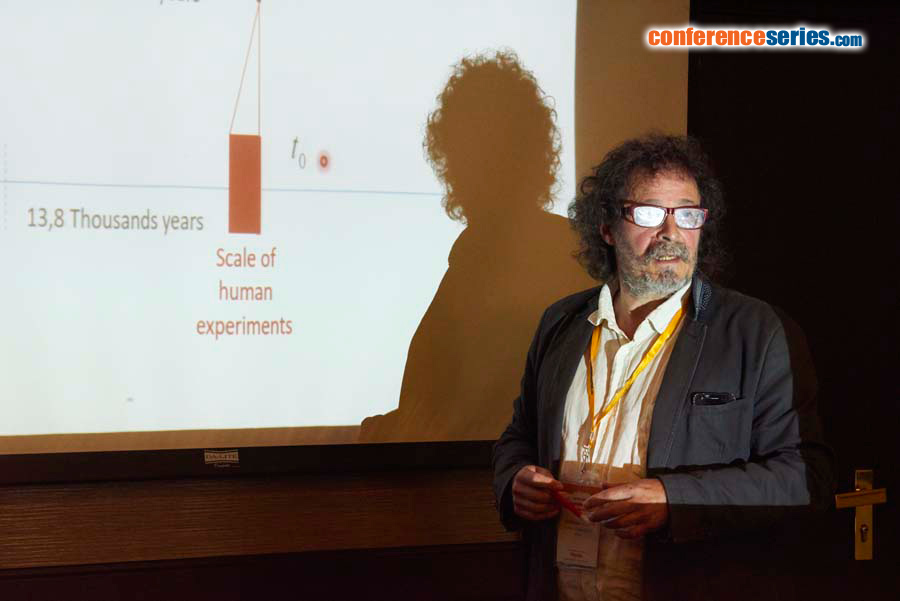
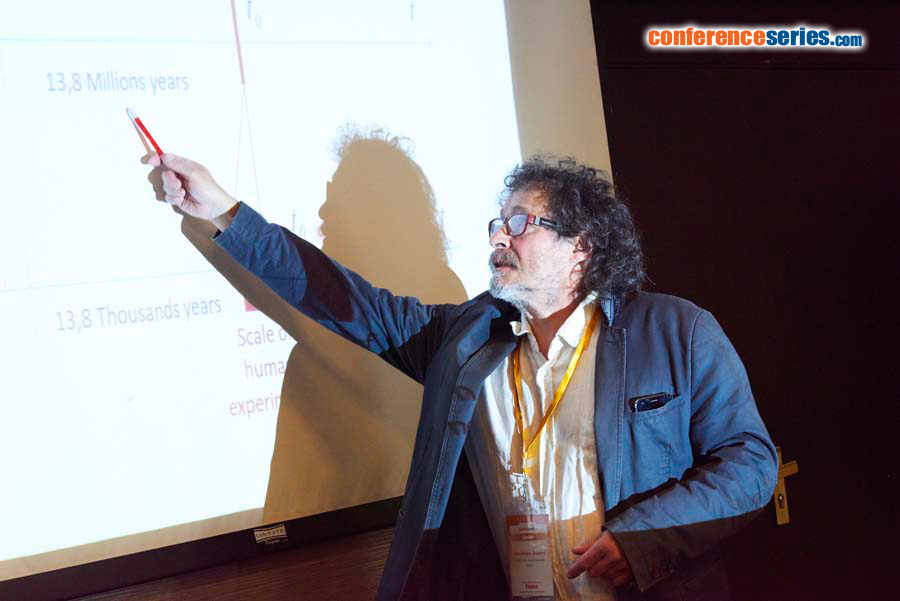
An irreversible phenomenon are characterized by a monotonic parameter of (universal) time t. According to philosophers, time cannot be defined without a reference to itself. We contest this because time is also a monotonic function of any irreversible parameter, from which time can be defined as well. Since universe expansion is a commonly accepted irreversible process, the average density of the universe 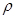 is a good candidate. Therefore we can define
is a good candidate. Therefore we can define 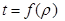 . Then the choice of the monotonic (and continuous) function f is open. In the absence of additional requirement, we can defnine A time
. Then the choice of the monotonic (and continuous) function f is open. In the absence of additional requirement, we can defnine A time 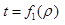 and another time
and another time 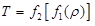 . Additional requirements will come from some physical hypothesis, such as inertia priniciple. It is a physical axiom, hopefully coherent with our everyday intuition and vocabulary. Every alternative definition of a time will lie on different physical rules and lead to different physical equations. Simpler than defining time is switching from one time to another. One can chose such a tranformation f2 (we will say mapping) in order that the impact on our equations is minimal at the human scale, which means in order that the two times t and T coincide over the short period of our existence. I will propose such a tranformation. It has amazing effects: for instance, within time T, the age of the universe becomes infinite. Beside a playful attempt to introduce some doubt in the apparently safest conceptual areas, the goal of this talk is to get the feedback of experts in astrophysical and comological models about the connexions they can infer between such time manipulation and the fundamentals of their models.
. Additional requirements will come from some physical hypothesis, such as inertia priniciple. It is a physical axiom, hopefully coherent with our everyday intuition and vocabulary. Every alternative definition of a time will lie on different physical rules and lead to different physical equations. Simpler than defining time is switching from one time to another. One can chose such a tranformation f2 (we will say mapping) in order that the impact on our equations is minimal at the human scale, which means in order that the two times t and T coincide over the short period of our existence. I will propose such a tranformation. It has amazing effects: for instance, within time T, the age of the universe becomes infinite. Beside a playful attempt to introduce some doubt in the apparently safest conceptual areas, the goal of this talk is to get the feedback of experts in astrophysical and comological models about the connexions they can infer between such time manipulation and the fundamentals of their models.


